Understanding Various Types of Masonry Techniques
The Highlights
- Masonry Matters: Key to durability, aesthetics, and energy efficiency in construction.
- Top Materials: Brick (versatile), Stone (durable), Concrete Blocks (cost-effective).
- Key Techniques: Veneer (decorative) vs. Solid (structural); Load-Bearing vs. Non-Load-Bearing walls.
- Modern Advancements:
- 3D Modeling – Enhances precision and reduces errors.
- Prefabrication – Increases efficiency and consistency.
- Green Building Materials – Promotes sustainability with recycled and energy-efficient options.
- Future Trends: Mixed-material designs, intricate brick-laying patterns, and sustainable innovations are shaping the future of masonry.
Masonry is a cornerstone of the construction industry. It’s a craft that combines artistry with engineering. Understanding various types of masonry techniques is crucial for anyone involved in property management or construction. The choice of masonry can significantly impact a building’s durability, energy efficiency, aesthetics, and even its value.
We’ll explore different materials like brick, stone, and concrete blocks. We’ll also discuss various construction techniques, from traditional methods to modern advancements. We’ll also highlight the role of technology and sustainability in masonry. How are innovations like 3D modeling and green building practices reshaping this age-old craft?
Whether you’re a property manager, a construction professional, or simply a design enthusiast, this guide will help you navigate the intricates of masonry and its techniques.

The Significance of Masonry in Construction
Masonry plays a vital role in constructing both residential and commercial buildings. Beyond structural integrity, masonry contributes significantly to a building’s aesthetic appeal. Various masonry materials, like brick and stone, each have unique textures and colors, allowing for creative architectural expression. This artistic versatility supports diverse design visions across projects.
Masonry is not merely about strength and beauty. It also enhances a building’s energy efficiency and fire resistance.
Masonry isn’t just strong and functional—it also has cultural and historical value. Traditional techniques have been passed down for generations, preserving heritage skills and keeping a link to the past. This craftsmanship still shapes modern construction, blending old and new building methods.
Common Masonry Materials and Their Properties
Masonry construction utilizes a variety of materials, each with distinct characteristics. Understanding these materials is key to choosing the right one for your project. The selection process considers factors such as durability, aesthetics, and cost.
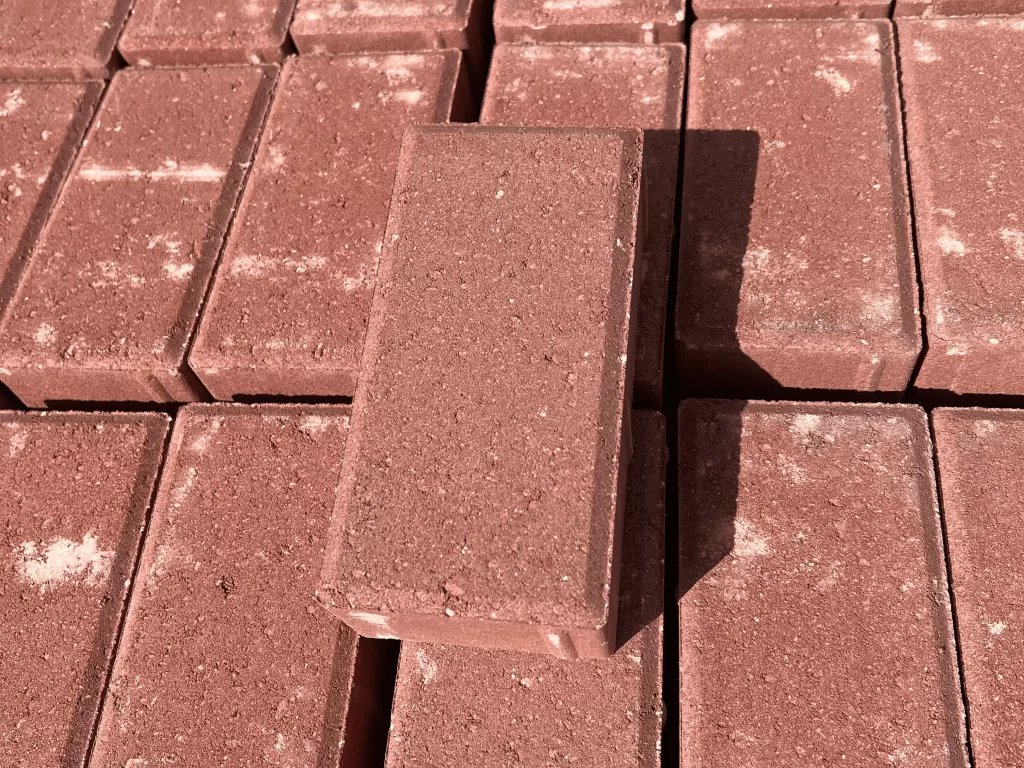
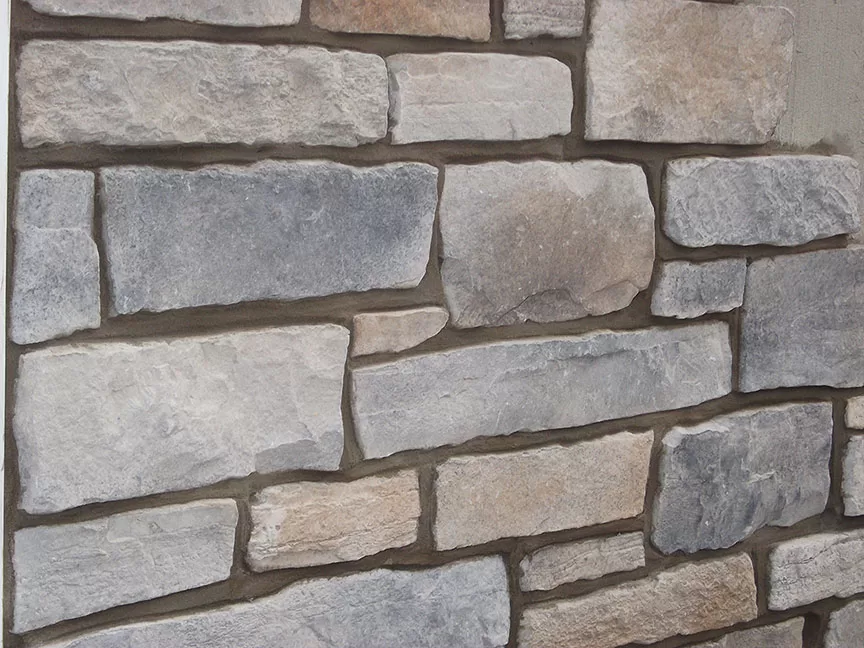
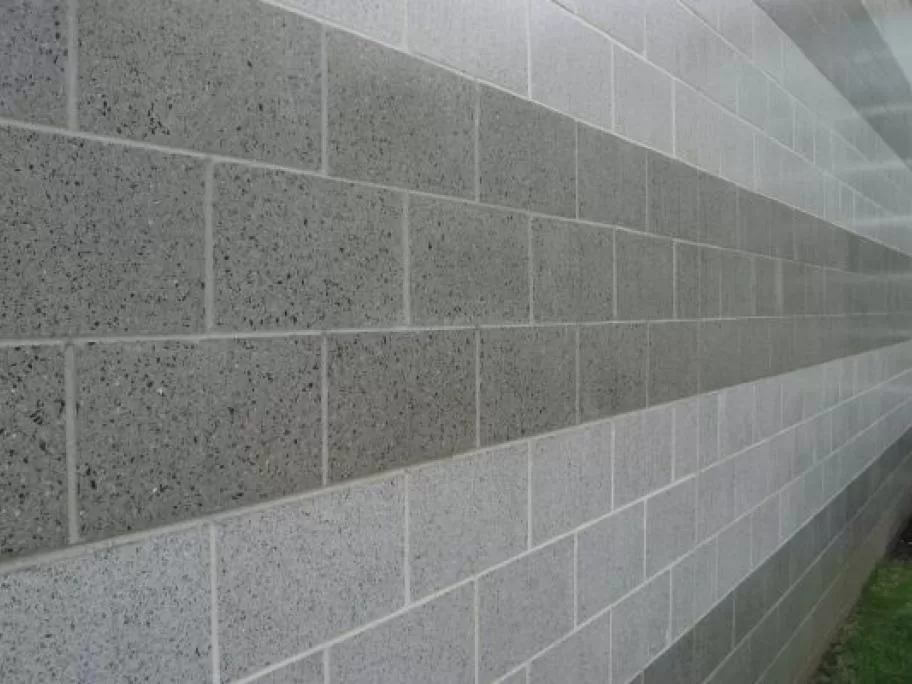



One of the most popular masonry materials is brick, known for its durability and timeless appeal. Bricks are available in a wide range of colors and sizes. Their versatility makes them a favorite choice for many construction projects.
Stone offers unparalleled natural beauty. It provides strength and durability, suitable for both traditional and modern design contexts. Different stone types offer varied textures and colors.
Concrete blocks are valued for their strength, uniformity, and affordability. They offer excellent thermal insulation properties, contributing to energy efficiency. Used in a variety of applications, concrete blocks provide substantial structural support.
Brick Stone
Brick is a solid, standard choice in masonry construction. Its unmatched in durability and versatility. Bricks are manufactured using clay, sand, and water, fired at high temperatures for strength.
This material’s natural thermal qualities help maintain comfortable indoor temperatures. As a result, brick masonry is energy-efficient, reducing heating and cooling costs. The extensive color range enhances creative options for designers and architects.
Additionally, brick offers excellent fire resistance, adding an essential safety feature. Regular maintenance ensures bricks retain their structural integrity and aesthetic appeal over time. This maintenance involves inspecting mortar joints and cleaning surfaces as needed.
Natural Stone

Natural stone embodies timeless elegance and strength. Sourced from quarries, stones like granite, limestone, and slate are used in masonry for centuries. Each type offers distinct textures and colors, complementing diverse architectural styles.
Stone is celebrated for its longevity and low maintenance requirements. Its innate durability makes it resistant to weathering and wear, ideal for various climates. Moreover, stone’s natural insulation properties contribute to energy-efficient building designs.
The environmental benefits of natural stone are significant. As a naturally occurring material, it has a low environmental impact when sourced responsibly. Its aesthetic appeal and performance make natural stone a favored choice for sustainable construction.
Concrete Blocks

Concrete blocks offer a practical solution in modern masonry construction. Made from cement, sand, and aggregates, they provide superior strength and uniformity. Their cost-effectiveness makes them a staple in both residential and commercial projects.
One notable advantage of concrete blocks is their thermal mass. This property helps regulate indoor temperatures, improving a building’s energy efficiency. Concrete blocks also provide sound insulation, enhancing the comfort of living and working spaces.
Concrete blocks are versatile, used for structural walls, partitions, and load-bearing applications. Despite their inherent durability, it is crucial to protect them from water infiltration to prevent degradation. Proper sealing and waterproofing measures enhance their longevity.
Masonry Types and Construction Techniques
Masonry techniques vary widely, offering diverse applications and finishes. Understanding these methods helps in selecting the most suitable approach for each project. The effectiveness of masonry construction often depends on the chosen technique and its execution.
Here are some common masonry techniques:
Veneer masonry for decorative exteriors.
Solid masonry for durable structures.
Load-bearing walls for structural support.
Non-load-bearing walls for space division.
Various bonding patterns for design diversity.
Modern construction integrates these techniques to achieve optimal results. Proper application of these methods addresses both aesthetic desires and practical needs, ensuring longevity and visual appeal.
Veneer vs. Solid Masonry
Veneer masonry serves as an exterior facade, not contributing to structural support. It’s often chosen for its design flexibility and ease of installation. The underlying frame provides the necessary structural integrity, complemented by the veneer’s appearance.
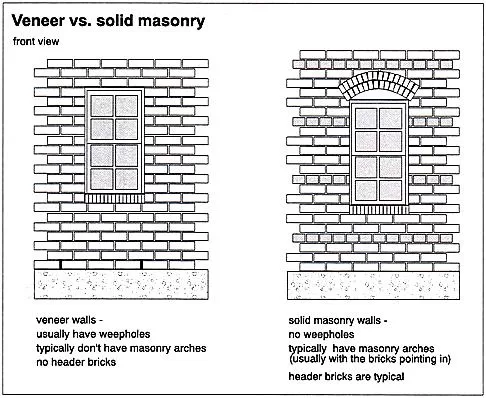
Solid masonry contrasts by forming the core of the structure. Each layer of masonry contributes to the building’s overall strength. The method is highly durable and resistant to environmental factors like weather and fire, but it demands more material and labor.
Load-Bearing vs. Non-Load-Bearing Walls
Load-bearing walls are integral to structural stability. They support floors, ceilings, and upper-level loads, essential in multi-story constructions. These walls require careful design to ensure they meet specific load requirements, often crafted with reinforced materials.
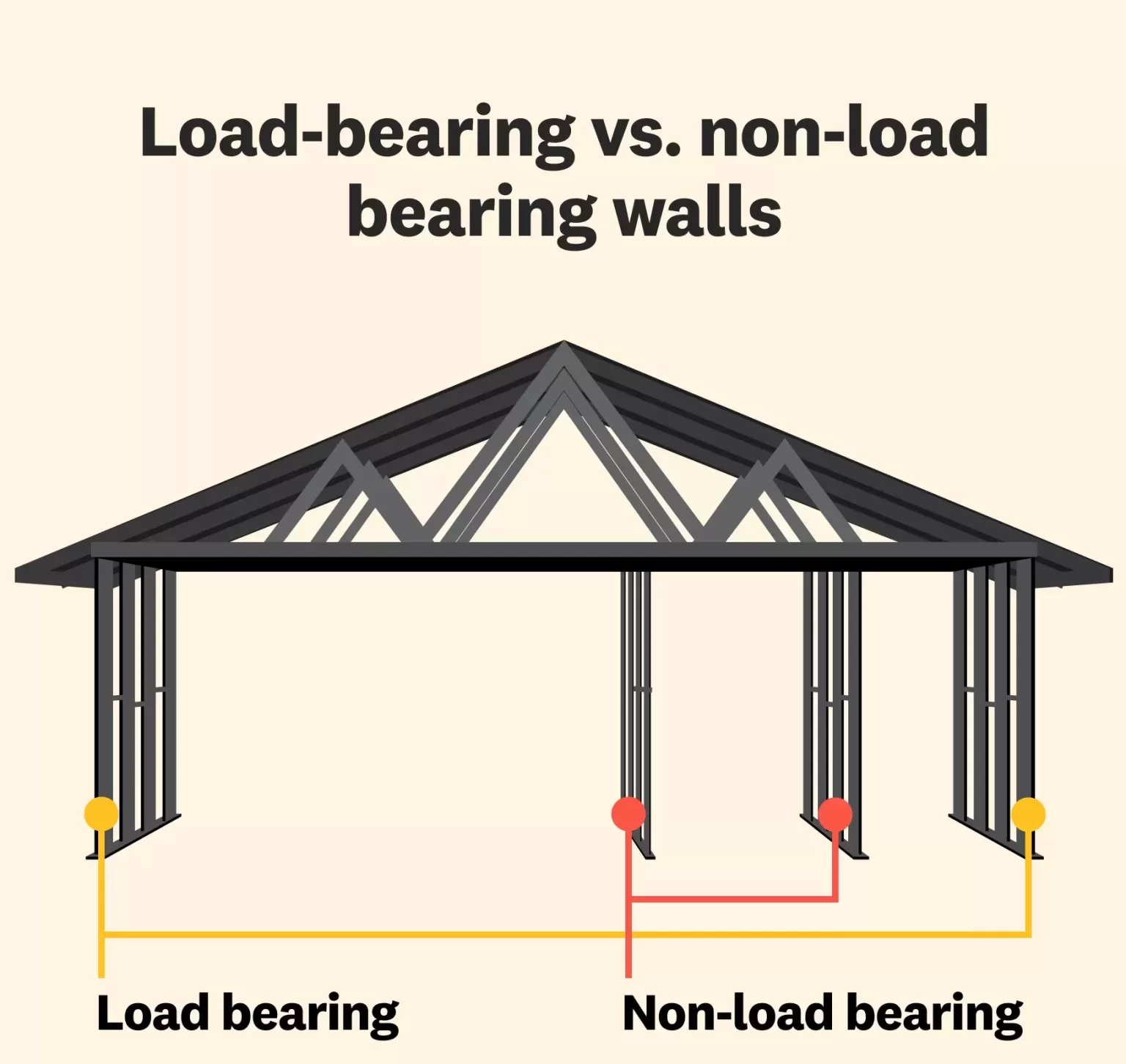
Non-load-bearing walls, however, do not support structural loads. They serve primarily as interior partitions, allowing for versatile space reconfiguration. Their lightweight construction reduces material cost and enables easy removal or modification.
Masonry Bonding and Patterns
Effective masonry relies on proper bonding techniques. The alignment of bricks or stones impacts structural stability and visual interest. Bonds like running, stack, and header adjust the overlap of units, enhancing the wall’s cohesion and aesthetic.
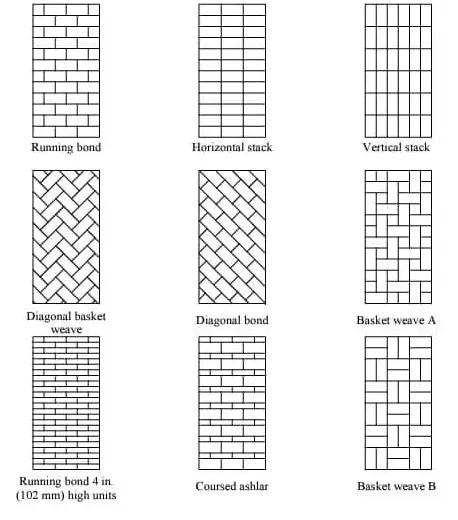
Patterns introduce visual variations in masonry walls, affecting load distribution. Patterns like chevron or basketweave offer distinct styles and structural benefits. Selecting the right pattern can highlight architectural features, adding depth and character to designs.
Advancements in Masonry
In recent years, masonry has embraced technological advancements. These innovations streamline processes and improve precision in construction. Technologies like 3D modeling revolutionize how we approach masonry projects.
As technology evolves, masonry techniques continue to adapt. This evolution ensures masonry remains relevant in contemporary construction.
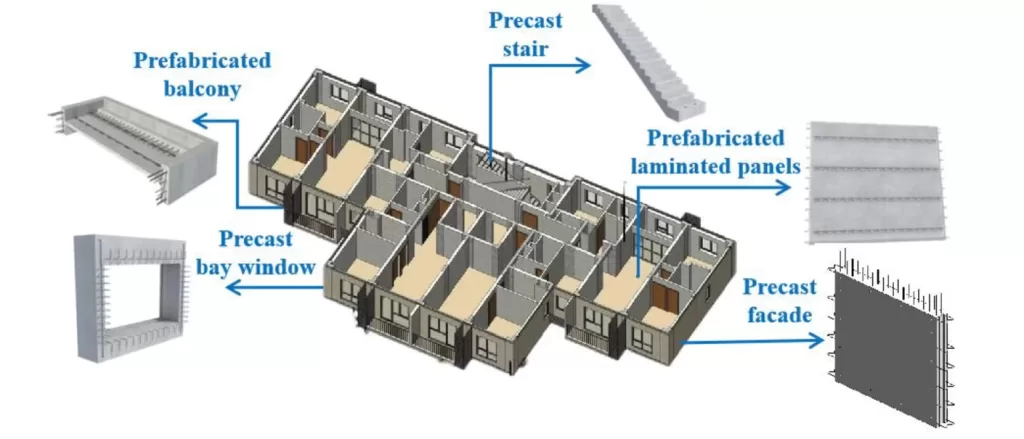
3D Modeling and Prefabrication
3D modeling allows architects to visualize projects before construction begins. It aids in planning intricate masonry details accurately. This technology significantly reduces errors and saves time.
Prefabrication, on the other hand, offers efficiency. Components are built off-site and assembled on location, reducing construction time. This method ensures consistency and quality in masonry elements, enhancing overall project execution.
Green Building and Sustainable Materials
Green building principles prioritize sustainability throughout the masonry process. They utilize recycled materials, minimizing environmental impact. These practices promote energy efficiency in construction.
Sustainable materials in masonry, such as recycled aggregates, decrease resource depletion. They offer durability and resilience, extending the lifespan of structures. Such materials align with global sustainability goals, making masonry an integral part of eco-friendly design.
Trends and Innovations in Masonry Design
Masonry design is constantly evolving, incorporating new materials and creative techniques. Mixed-material designs are gaining popularity, offering unique aesthetics and improved functionality. Combining brick, stone, and glass, for example, achieves striking modern designs.
Innovative textures and patterns in masonry are also trending. Designers are experimenting with intricate brick laying patterns that enhance visual appeal. These techniques create dynamic facades that catch the eye and create a lasting impression.
Sustainability is a key driver in masonry innovation. Use of recycled materials is becoming standard in eco-friendly projects. Sustainable masonry options not only reduce environmental impact but also enhance energy efficiency, benefiting both the environment and building occupants.
The Future of Masonry in Construction
Masonry remains a cornerstone of construction due to its enduring resilience and flexibility. The integration of advanced technologies and sustainable materials is shaping its future. These innovations enable designers to create energy-efficient and aesthetically pleasing structures.
Looking ahead, masonry’s role in green building practices will continue to grow. As the industry embraces sustainability, masonry will contribute significantly to sustainable construction techniques. This timeless building method is sure to adapt, innovate, and remain a vital element of architectural expression for years to come.
